
You wouldn’t hire a new employee without making sure they’re the right fit for the job, right? Just as employers thoroughly vet candidates, organizations across the financial services industry need to have a good read on their prospective clients before allowing them to open an account to mitigate fraud and money laundering risk. This is where customer due diligence comes into play.
What is Customer Due Diligence?
Customer due diligence (CDD) is the act of performing background checks and other screening on the customer to ensure that they are properly risk-assessed before being onboarded.
CDD is at the heart of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) initiatives. It helps banks and financial institutions prevent financial crimes like money laundering, terrorist financing, human and drug trafficking and fraud.
Why is CDD Important?
When you consider what’s at stake, it starts to make a little more sense why banks and other financial institutions are spending big money on AML compliance. These countermeasures are designed to thwart the growing threat of money laundering, which unfortunately isn’t a tactic used by drug cartels alone — it’s now being used across a broad range of criminal enterprises.
Here are a few reasons to take CDD seriously:
- Big Compliance Fines: Enforcement actions related to AML have been on the rise. Since 2009, regulators have levied billions of dollars in AML-related fines globally. Most of these have been against U.S. firms.
- Sophisticated Cyber Threats: Criminals are using more sophisticated means to remain undetected, including globally coordinated technology, insider information, the dark web and e-commerce schemes.
- Reputational Risk: AML incidents put a financial institution’s reputation on the line.
- Rising Costs: Most AML compliance activities require significant manual effort, making them inefficient and difficult to scale. In 2022, the cost of AML compliance for financial services firms across the globe equaled $274 billion per year.
- Poor Customer Experience: Compliance staff must have multiple touch points with a customer to gather and verify information. Perhaps not surprisingly, one in three financial institutions have lost potential customers due to inefficient or slow onboarding processes.
What Does the Typical CDD Process Look Like?
An effective customer due diligence program includes collecting a variety of customer information throughout the course of a company-customer relationship.
Customer Due Diligence Requirements
- Customer Information: To ensure customers are who they say they are, companies collect the customer’s full name, photo identification, address, phone number, email address, occupation, tax identification number and more.
- Business Information: CDD measures should include additional identifying information about the customer’s business model, source of funds and beneficial ownership.
- Customer Risk Profiles/Risk Assessments: Based on the customer’s identity, location and type of business, customers are sorted into different risk levels (usually low, medium and high) to indicate the level of money laundering risk they pose. A customer’s risk profile determines the required level of due diligence. High-risk customers need a more in-depth due diligence process than low-risk customers.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Customer due diligence doesn’t stop after you onboard the customer. CDD measures should include an ongoing monitoring system and keep an eye on higher-risk customers, suspicious transactions, changing customer profiles, etc.
Sample Customer Due Diligence Flow Chart
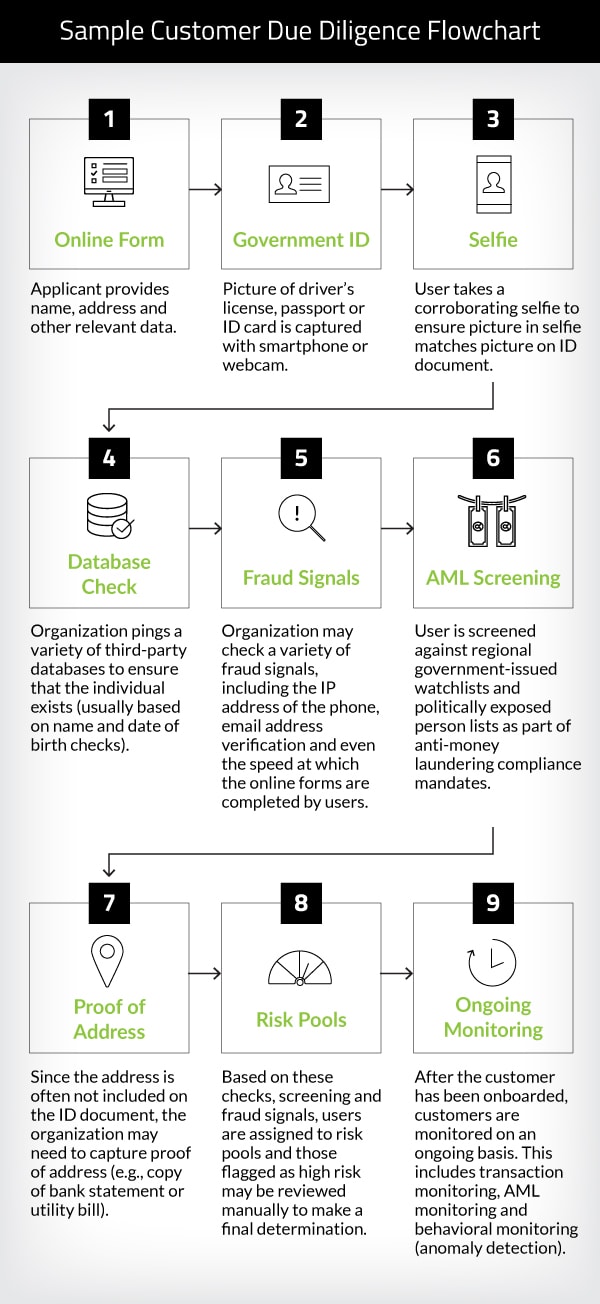
This sample flow chart walks through nine steps a financial institution may take as part of their KYC process. We’ve talked to hundreds of banks, and there seem to be hundreds of variations of how they perform customer due diligence. Your CDD workflow should answer these fundamental questions:
- Is the applicant the person they claim to be online?
- Does the risk profile of the applicant raise any red flags?
Low-risk individuals can be fast-tracked through the approval process. Thanks to automation of online identity verification and AML screening, this streamlined process can be vastly more efficient than traditional manual processes. This reduces the decision time to minutes, not hours or days.
However, decision time for higher-risk individuals may still take longer, between 48 and 72 hours, because of the extra review time needed to vet these individuals. Assuming that more than 90% of your applicants will fall into the low-to-medium risk pool, the cost and efficiency gains of automated identity verification and AML screening can have a dramatic reduction on AML costs and improvement in the user experience.
Streamlining the Customer Due Diligence Process
Complying with KYC and AML requirements has made the account opening process a long and complex journey for corporations. And thanks to increasing regulations, the customer onboarding process is only getting worse.
Moreover, increased onboarding time and friction leads to higher abandonment rates by legitimate customers. These costs can often far exceed the cost of any perpetrated fraud when one considers the lifetime value of those lost or abandoned customers.
This is why organizations are taking steps to streamline the CDD process to save money, time and customers.
Identity Verification
While there are a number of alternative verification methods, more and more companies are now relying on automated identity verification to smooth out and speed up the onboarding process for new customers.
Automated identity verification relies on AI, machine learning and biometrics to validate passports and driver’s licenses, check against the customer-provided selfie and, in some cases, perform a liveness check to ensure the applicant is physically present and not spoofing the system with a picture of someone else or using a doctored video.
Ongoing Monitoring and Screening
Just as you score individuals and put them into risk categories during the identity proofing stage, you should monitor and update the customer’s risk rating throughout the customer lifecycle.
By continually checking and pinging established (and constantly refreshed) databases (including OFAC, HMT, UN and thousands of other government, regulatory, law enforcement, fitness and probity watchlists), financial institutions can be notified immediately via an alert. If a customer appears on one of these PEPs and sanctions lists, they can mitigate risk and take appropriate next steps. This ensures that the company is kept informed of any status changes to their existing customer base in real time.
Better identity verification and AML screening solutions are enabling financial institutions to meet the requirements of regulators, banking partners and auditors with an electronic audit trail of all system and user actions with date and time stamps. These solutions help financial institutions spot patterns and outliers by monitoring current transactions alongside historic transaction and behavior data.
Risk Management
As businesses take a risk-based approach to assessing a customer’s profile before and after joining the organization, customer due diligence helps to assess risk by gathering comprehensive information about customers. This, in turn, enables businesses to make informed decisions and create an effective risk management process.
Conducting CDD ensures compliance with regulations and legal obligations and protects businesses from penalties and reputational damage. CDD also safeguards against financial losses by identifying high-risk customers and implementing appropriate risk mitigation measures.
Digital Trust Throughout the Customer Journey
How to Leverage the Jumio KYX Platform from Onboarding to Ongoing Monitoring
When is Customer Due Diligence Required?
The application of customer due diligence is required when a firm that is covered by money laundering regulations enters into a business relationship with a customer or a potential customer. This includes occasional one-off transactions even though this may not constitute an actual business relationship.
A customer/business relationship forms when two or more parties engage for the purposes of conducting regular business or to perform a one-off transaction. The term “business relationship” applies where a professional, commercial relationship will exist with an expectation by the firm that it will have an element of duration.
A More Enlightened Approach to CDD
A growing number of banks and fintechs are discovering how to automate their CDD (and, if necessary, enhanced due diligence) processes resulting in a vastly better customer experience and a dramatic reduction in online abandonment rates. By utilizing advanced tools like Jumio’s Identity Verification and AML Solutions, financial institutions can easily meet their regulatory requirements without sacrificing customer experience.
Learn more about how you can streamline your onboarding and ongoing monitoring CDD measures with Jumio.
CDD FAQs
What are the 4 customer due diligence requirements?
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) involves four key requirements:
- Identifying and verifying the customer’s identity using reliable sources
- Understanding the nature of the customer’s business relationship to determine expected transactions.
- Ensuring ongoing monitoring of the customer’s transactions for suspicious activities
- Maintaining comprehensive records of the CDD process and transactions
What are the 3 types of customer due diligence?
The three types of Customer Due Diligence (CDD) are:
- Simplified CDD, which applies to low-risk customers
- Standard CDD, which involves basic identity verification
- Enhanced CDD, which is conducted for high-risk customers and involves in-depth identity checks and source of funds verification.
What are red flags in CDD?
Red flags in Customer Due Diligence (CDD) are warning indicators of potentially suspicious or high-risk activities. These can include unusual transaction patterns, inconsistent identification details, transactions involving high-risk jurisdictions, complex ownership structures, or reluctance to provide necessary information. Recognizing and addressing these red flags is crucial for effective risk management and compliance.
What are the CDD requirements required by law?
CDD requirements mandated by law vary across jurisdictions, but common elements include identifying and verifying the customer’s identity, understanding the nature of the customer’s business, assessing the customer’s risk profile, and monitoring transactions for suspicious activities.
Additionally, compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) regulations, such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations, is often a fundamental requirement for conducting CDD.
Is CDD different from EDD?
Yes, CDD (Customer Due Diligence) and EDD (Enhanced Due Diligence) are distinct concepts within the context of risk management. CDD refers to the standard process of gathering customer information, verifying identities and assessing risks. EDD is a more comprehensive and in-depth form of due diligence applied to customers with a higher risk profile. EDD involves additional measures, such as conducting more extensive background checks, verifying the source of funds and applying enhanced monitoring to mitigate heightened risks.
Can customer due diligence help detect suspicious activity?
Yes, customer due diligence plays a crucial role in detecting suspicious activity. By conducting thorough CDD, organizations can collect relevant customer information and assess their risk profile. This enables the identification of potential red flags or anomalies that may indicate suspicious behavior, such as inconsistent financial transactions, unusual business activities, or connections to sanctioned entities. CDD provides a foundation for ongoing monitoring and detection of suspicious activity, which aids in the prevention of financial crimes including money laundering, fraud and terrorist financing.
Originally published October 19, 2021; updated October 27, 2023

